Bear Market vs. Bull Market: Key Differences and Indicators
Are you an investor looking to expand your knowledge of the stock markets and navigate them more efficiently? Understanding the differences between a bear market and a bull market is essential for any serious investor who wants to potentially maximise their investment return. Bear markets, characterised by falling prices over time, require different approaches than bullish markets to achieve financial success.
In this article, we will look at what differentiates bear and bull performance indicators, discuss vital distinctions between these two environments, and explain how one can use them to make informed decisions for their investments. So please read carefully as we break down everything you need to know about bearing vs. bulling in the stock market.
Defining the Terminology of Bear and Bull Markets
The financial world is complex and ever-changing, with terms and phrases being thrown around with little explanation. Two of the most commonly used terms in the investing world that confuse are the bull and bear market. Knowing and understanding the meaning of these terms is vital for both experienced investors and beginners.
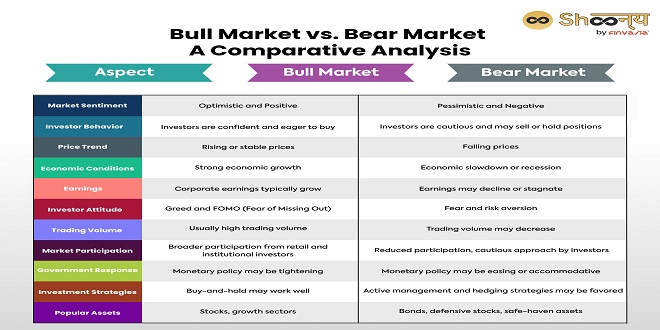
A bull market occurs when the stock market or a particular stock is experiencing long periods of growth and prosperity. On the other hand, a bear market is when stock prices drop, and the investors sell their shares, leading to a pessimistic attitude. Learning the ins and outs of these terms allows investors to make informed decisions and potentially achieve favourable outcomes.
Examining the Different Indicators of a Bear or Bull Market
Understanding the various indicators of a bear or bull market is crucial for predicting which direction the stock market may be headed. Here are some critical differences between these two types of markets. In a bull market, investors see stock prices rising steadily and have confidence in the economy’s growth, leading to more investments. Conversely, when stocks fall in value over time, it is referred to as a bear market. Investors are wary of their investments and tend to sell their shares to avoid further losses.
Moreover, trading volumes indicate whether the market is bullish or bearish. In bull markets, trading volumes are high due to increased investor activity and economic confidence. However, in bear markets, trading volumes decrease as investors become more cautious and risk-averse.
Another key indicator of a bull market is the performance of different sectors. During a bullish trend, most sectors outperform, meaning there are opportunities for gains in various industries. In contrast, bear markets affect all sectors negatively, making it challenging to find profitable investments.
Analysing Historical Trends to Predict Future Movements in the Market
One of the most effective ways to predict future market movements is by analysing historical trends. Investors can make educated guesses on how the market may behave by looking at past data and patterns. In a bull market, studying past trends can help identify potential entry points for investments and maximise profits.
On the other hand, studying historical data in a bear market can provide valuable insights into when it may be an excellent time to sell investments and cut losses. Remembering past performance does not guarantee future results, but analysing historical trends can help investors make more informed decisions.
What Factors Impact Bear and Bull Markets
Various factors exert influence on the performance of bear and bull markets. Economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and GDP growth, play a significant role in shaping stock prices. In a bullish market, robust economic conditions contribute to investor confidence and stimulate increased investments. On the other hand, during a bear market, poor economic conditions may induce investors to adopt a more risk-averse approach, causing hesitancy towards investment.
In addition to economic conditions, other factors such as political stability, consumer sentiment, and company earnings contribute to market performance. Political stability provides a favourable environment for businesses to thrive, instilling confidence in investors. Similarly, consumer sentiment, reflecting consumers’ general outlook and sentiment, can impact market dynamics. Positive consumer sentiment leads to increased consumer spending and potentially higher company earnings, which can drive market growth.
Exploring Different Strategies to Take Advantage of Each Market Type
As an investor, it is essential to have a diverse portfolio that can weather any market conditions. In a bull market, investors may consider utilising strategies such as trend following or momentum investing, where they ride the upward trend of stocks and sell before the market starts declining. On the other hand, in a bear market, investors may opt for defensive strategies such as value investing or dividend investing.
Value investing involves identifying undervalued stocks and purchasing them at a discounted price, assuming their value will increase. Similarly, dividend investing focuses on investing in companies with a history of paying dividends consistently, providing investors with a steady income stream even during market downturns.




